Product Environmental Management(Eco-Products)
Basic Stance
Improving Environmental Friendliness and Efficiency in Product Functions
In consideration of the environment, DENSO believes that an advanced automotive society firmly maintains a balance between caring for the environment and enjoying the full potential of the vehicle. To realize an advanced automotive society, DENSO seeks to enhance functions such as safety, maneuverability, comfort, and other aspects while working to reduce the environmental impact throughout a vehicle’s life.
Specifically, we:
(1) develop products geared toward xEVs that help reduce CO2 emissions when driving, including products for BEVs, PHEVs, HEVs, and FCEVs;
(2) develop products that contribute to enhanced fuel efficiency in vehicles, such as engine management systems, and idling stop systems; and
(3) develop products that contribute to enhanced fuel efficiency in harmony with social infrastructures, such as car navigation systems.
All DENSO products aim to create new value that provides enhanced comfort and convenience for customers while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, resource consumption, and the risk of chemical substance pollution. This rationale is based on the approach to environmental efficiency recommended at the 1992 Earth Summit.
In addition, with regard to CO2 emissions, we aim to help realize carbon neutrality, a trend that is accelerating in global society, through our mobility products and energy use. Specifically, we are striving to reduce CO2 emissions from our mobility products to the greatest extent possible. We are also working to achieve negative CO2 emissions through the establishment of technologies to capture, recycle, store, and reuse CO2. By doing so, we will contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society.
Specific Initiatives
Product Development Techniques That Anticipate the Entire Life Cycle
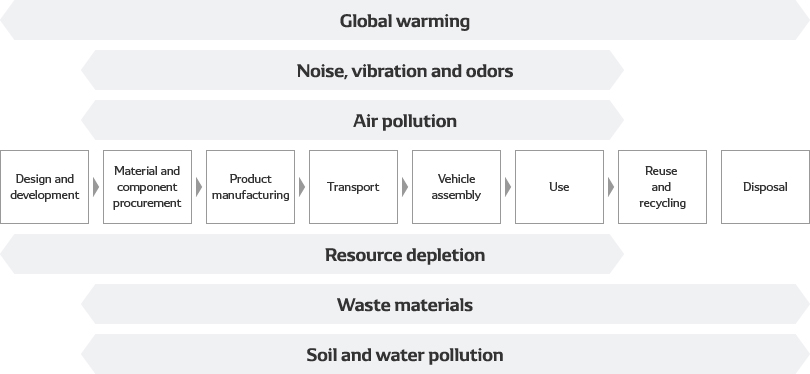
DENSO ascertains the balance between product value and environmental impact using Factor Delta environmental factors and sets targets for each product (Plan step). We then conduct a life cycle assessment (LCA) to determine environmental friendliness and impact at the design stage (Do step). The extent to which these targets are met is checked at a Quality Assurance Meeting, a milestone in the design process (Check step), and the results are reflected in the development of upcoming models (Act step).
Environmental impact during the automotive component lifecycle
Operation of Factor Delta
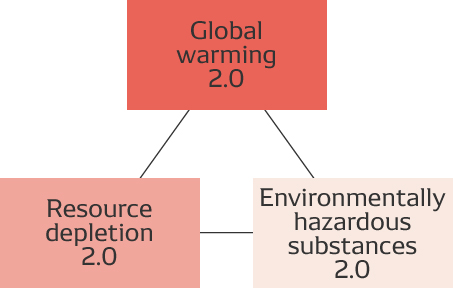
The multiplier at which environmental efficiency for evaluated products is increased relative to standard products is known as an “improvement factor.”
DENSO has collaborated with the Japan Auto Parts Industries Association (JAPIA) to develop a reasonable method for calculating this factor for automotive components, and these efforts have been summarized in the series of Guidelines for Environmental Factors for Products. Based on Japan’s Basic Environmental Law, these guidelines provide a means for calculating indices linked to product value in the form of positive factors and negative factors related to global warming, resource depletion, and emissions of environmentally hazardous substances throughout the automotive part life cycle.
In conjunction with the above indices, in fiscal 2011 we collaborated with JAPIA to formulate the JAPIA life cycle inventory *1 calculation guidelines and calculation rules in an effort to efficiently calculate the environmental burden during the manufacture and use stage in the extremely complex supply chain for the automotive parts industry. These activities have garnered high praise, receiving the Award of the Director-General of the Industrial Science and Technology Policy and Environment Bureau (METI) at the LCA Japan Forum *2 Awards in March 2018.
*1 Life cycle inventory (LCI) is a method for calculating the level of environmental burden of a product throughout its life cycle.
*2 The LCA Japan Forum was established in 1995 to encourage and expand life cycle assessments (LCA)*3 and environmentally efficient business approaches and to realize sustainable economic and social growth. Please see the link below for details on the LCA Japan Forum Awards.
http://lca-forum.org/commendation/2017.html (Japanese only)
*3 Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a method for assessing the impact of a product on the environment based on the results determined through LCI.
Calculation of Factor Delta indices
Note: Indices must be calculated in an objective manner so that they can be accepted by a majority of people. DENSO has based its method on the concept of factors proposed in the 1990s by researchers worldwide and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Indices are calculated in a positive way by calculating the environmental efficiency of the product or service in question and evaluating technological progress in a forward-looking manner by means of the improvement factor.
| Overview of key product and function |
Power control unit for hybrid automobiles |
|---|---|
| Factor Delta (Enhancement of environmental performance) |
|
| Principal value improvement |
33% smaller than conventional units installed in the Toyota Prius due to cooling structure improvement and electric control circuit integration. |
| Principal impact on environment |
Reduces switching loss and steady loss in insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) by approximately 20% compared with conventional units installed in the Toyota Prius |