Quality Control
Basic Stance
Since its founding, the DENSO Group has been dedicated to providing safe, high-quality services that will satisfy customers and earn their trust based on a commitment under the DENSO Group Sustainability Policy. We have designated the thorough implementation of the Quality First principle, the practice of quality assurance from the beginning of production and the promotion of quality control with full employee participation as basic quality assurance policies. We are committed to carrying out the Quality First principle in creating products.
Additionally, based on information collected by sales and technology departments from customers, we are continuously making efforts to ensure that our customers are satisfied with our level of quality.
Promotion Structure
In order to provide the best products for customers around the world, the DENSO Group has established technical centers in Japan, the United States, Germany, Thailand, China, India, and Brazil. In doing so, the Group has put into place a global structure that allows for product development, quality testing, and quality evaluation to be carried out in accordance with the characteristics of each region.
Furthermore, the DENSO Group has completed the acquisition of IATF 16949 certification, an international standard for quality management systems in the automotive industry.
Quality assurance policies and systems
Specific Initiatives
Reinforcement of Fundamental Quality Technologies
Through our quality control promotion structure, centered on specialists, in each technological field we are working to address the extremely challenging quality-related issues that we currently face. At the same time, we are taking the lead in developing quality-related technologies in our focus fields (automated driving, electrification, carbon neutrality, and fuel cells, etc.) with attention to future changes in the operating environment. By applying such technologies in the development of new products, we are striving to prevent future quality-related issues.
Quality control of new products—Product development that places safety assurance as its top priority
For the quality assurance process of new products, specialized departments such as quality control and production technology are undertaking unified efforts to strictly check quality by visualizing the degree of product completion as well as quality-related risks.
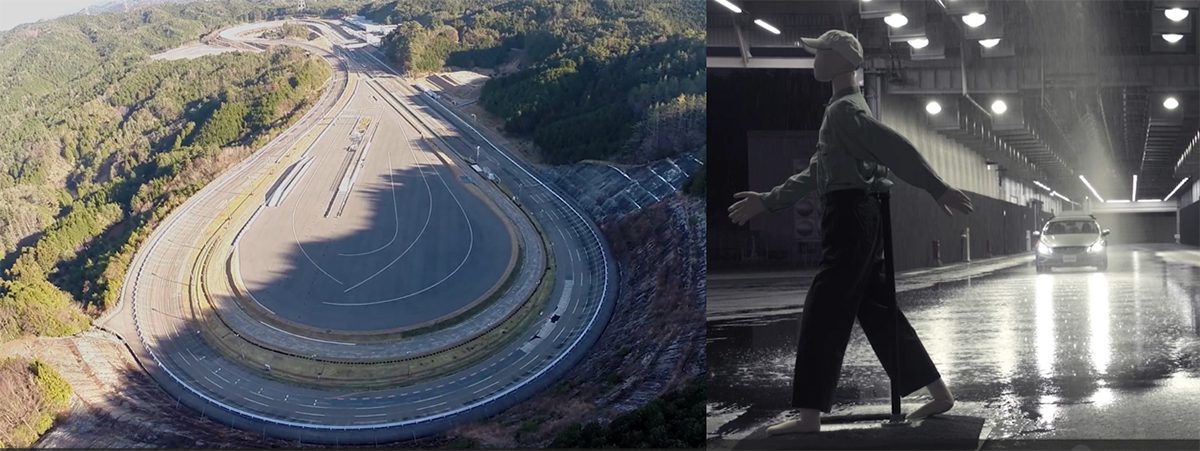
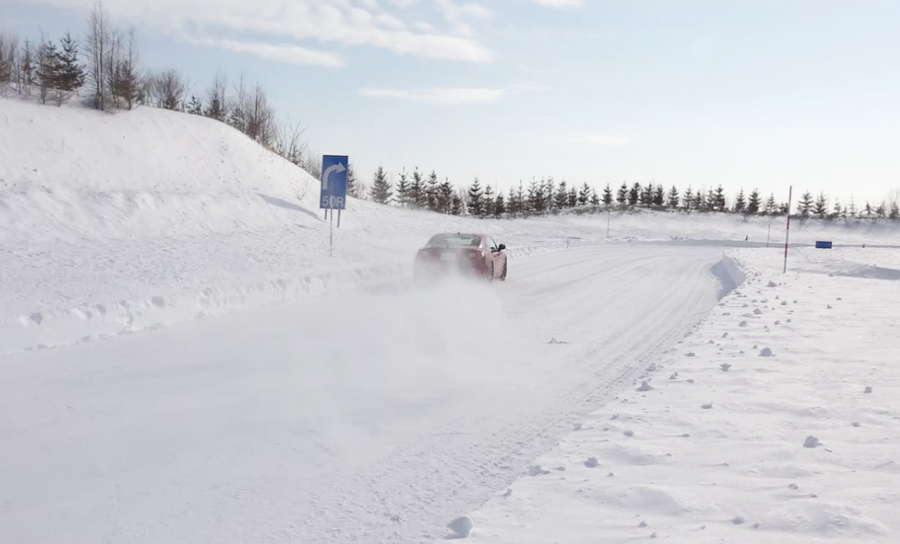
Design departments thoroughly employ safety designs, such as fail-safe designs,*1 and conduct safety evaluations. They also promote system and product design pursuant to ISO 26262 certification for functional safety. Particularly, for the design stage, in order to assure high reliability and durability, we repeatedly conduct in-vehicle testing under a range of conditions such as high-speed driving, rough roads, low temperatures and icing on our test course, as well as various tests in our environmental testing room. In these ways, we carefully verify product quality.
Furthermore, from product planning to production and shipment, functional departments clearly specify operational procedures and responsible departments strictly monitor compliance with applicable laws and regulations in each stage. When launching new products in particular, the responsible departments are required to conduct safety evaluations based on internal regulations and to report on the results of legal compliance checks.
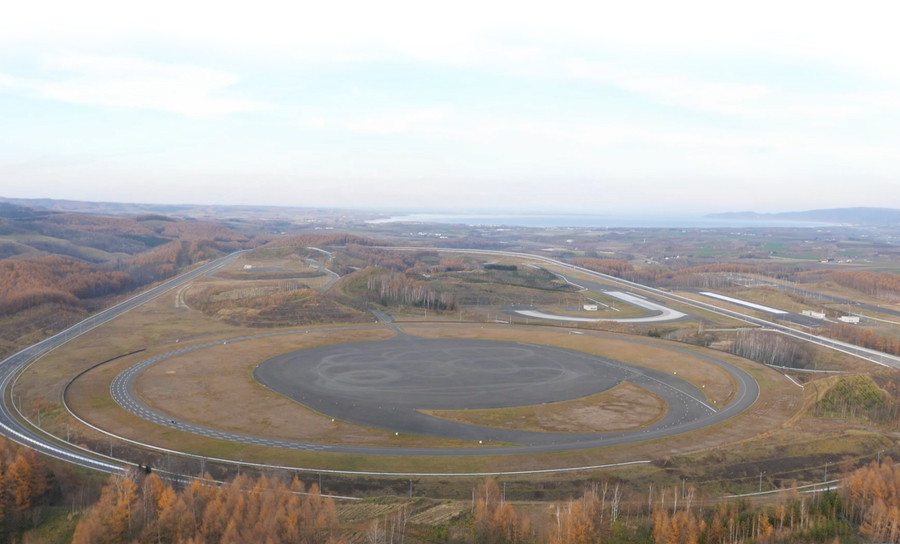
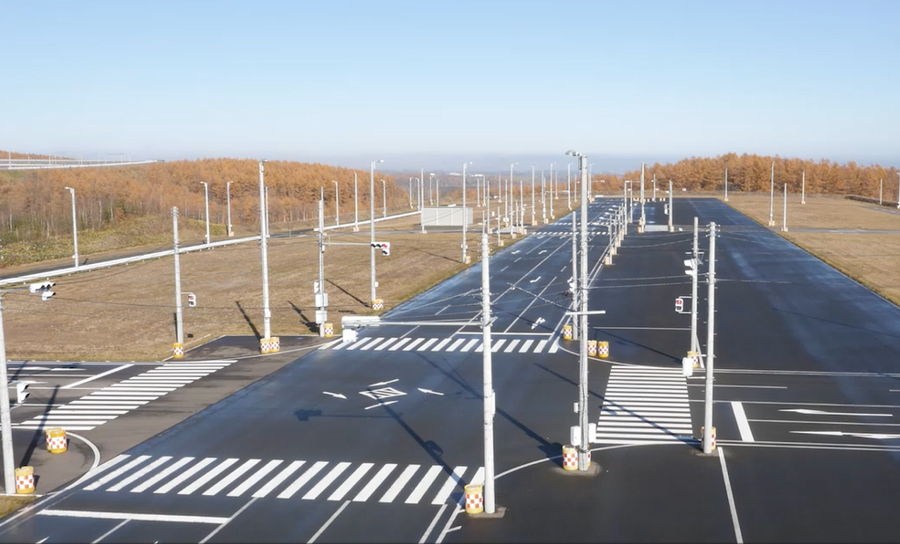
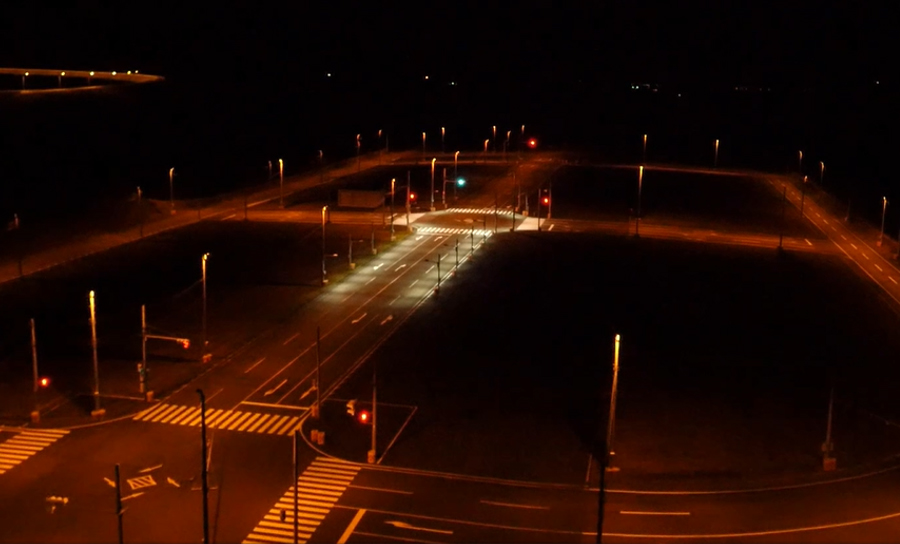
The Nukata Proving Ground (Aichi Prefecture) and the Abashiri Test Center (Hokkaido Prefecture), our in-house test courses, began using evaluation equipment in 2012 in anticipation of the need to evaluate actual vehicles equipped with driver assistance and automated driving technologies, and these two test courses have been refining this equipment each year in line with advances in these technologies.
*1 Fail-safe design: A design philosophy requiring products to be controlled in a safe manner in the event of an accident or erroneous operation
Nukata Proving Ground (Established in 1984) Size: 1,000,000 ㎡
Abashiri Test Center (Established in 2002) Size: 5,500,000 ㎡ (120 times the size of Tokyo Dome)
Quality Improvement Activities Leveraging Vehicle Data—Establishing Foundational Data Analysis Systems
When quality-related issues have arisen in the market, we have conventionally undertaken efforts to research their causes after collecting the defective products, in order to resolve the issues as swiftly as possible. At the moment, however, we are working to establish foundational systems to effectively analyze big data collected from vehicles, such as the driving conditions in the event of a defect as well as information on the surrounding environment and vehicle operational status, before we conduct a product recall. Through such systems, we will be able to automatically visualize and subsequently analyze vehicle control information in a highly effective manner in order to identify the cause of the problem. Going forward, we will strive to apply these foundational systems using AI-based technologies that identify causes of failure and detect signs of failure in advance, thereby further accelerating efforts to address failures and working to prevent them from happening in the first place.
Assessing the Quality Management Practices of Senior Management
At the time of our founding, we decided to compete on the basis of quality based on our assessment of the future trends in each region and market and the industry as a whole. To confirm the status of quality management practices by senior management, in 1960 we began conducting quality control analysis, which continues to be carried out to this day in our business divisions and Group companies in Japan and overseas once every two to three years.
This quality control analysis reviews the quality of our business strategies, systems, products, and services as well as management issues and the policies to address these issues concerning the DENSO Group’s Companywide priority measures. In addition, senior management and the business divisions and Group companies under examination engage in in-depth discussions on workplace culture, which underpins these measures, by conducting on-site diagnosis in an effort to further strengthen governance.
Education, training, and activities to raise awareness
The DENSO Group considers hitozukuri (human resource development) to be the foundation of its business and thus nurtures technical and skilled employees in a systematic and ongoing manner while also handing down the DENSO-style of monozukuri (manufacturing) through hands-on practical education and training.
Main Education Activities
-
Implementation of position-based educational activities on quality for new employees, second-year employees, and newly appointed division heads and managers
-
Establishment of the Quality Dojo, which fosters the technical capabilities of quality assurance personnel through practical education and discussions in small groups
-
Implementation of Monozukuri DNA Training, where employees slated to be seconded overseas gain practical education on the vital points of quality while working on imitation production lines
-
Adoption of e-learning materials and online training that can be received remotely at Group companies both in Japan and overseas
For over 10 years, we have been providing a broad range of learning opportunities related to AI and big data utilization. In addition, our engineers, administrative employees, and managers have all received literacy training so that they are able to make proper use of AI within their day-to-day work. Furthermore, through the AI Practical Application Dojo and other initiatives, we aim by the end of fiscal 2023 to cultivate 2,000 AI-savvy personnel who can make full use of AI at work.
Furthermore, we have developed tools that make it easy to utilize big data via a tablet device in order to reform our quality control activities in a manner that better suits the era of digital natives. Leveraging these tools, we commenced educational training geared toward users involving improvement activities based on deeper, previously unnoticed perspectives.
-
Introduction to Big Data Analysis
(excerpts from the introductory text) -
Big data visualization and analysis platform
(Able to conduct highly sophisticated analysis using machine learning, etc.,
without the need for programming)
Promoting Activities to Maintain and Improve Quality Assurance Together with Our Suppliers
To continue to offer products that satisfy its customers, DENSO needs to maintain and improve its quality assurance in collaboration with its suppliers, who provide the Company with components and other materials.
As a general prerequisite for entering into a basic business contract with suppliers, we ask that our suppliers promise to promote efforts to maintain and improve their quality assurance practices. At the same time, we provide support to suppliers to help them pursue these endeavors. By doing so, we confirm on an ongoing basis that the components and other materials supplied to us always meet the necessary level of quality.
〈Examples of Specific Initiatives〉
-
Formulated quality assurance manual for suppliers based on items required under the international quality assurance standard IATF 16949
-
Had suppliers implement self-inspections based on quality assurance check sheets (once a year) and carried out on-site inspections based on the results of these self-inspections
-
Established quality targets at suppliers and monitored their results (monthly)
-
Shared quality policies with major suppliers and suppliers (deemed as targets for priority support) for which there were quality-related concerns, etc. (yearly)
-
Implemented on-site verification at suppliers deemed as targets for priority support and offered advice and support for resolving issues
FEATURE: Rebuilding Our Foundation for Quality Management
DENSO has always taken a quality-first approach to manufacturing. However, in 2019 a quality-related issue occurred that was unprecedented in scale. This situation was taken very seriously by all of our employees, who have since worked together to enhance our knowledge and awareness and reform our organizational culture.

We have been conducting comprehensive inspections on our flow management and products under development on a Companywide scale, and are working to thoroughly uncover potential risks and eliminate technical issues, as well as promote automation and labor savings by consistently introducing new tools from the upstream to downstream stages of development, with the aim of enhancing our software quality.
These measures have produced results in the form of a decrease in the number of defects detected in our customers’ processes and in the marketplace as well as quality-related awards received from customers.
In accordance with our basic policy of meeting customer expectations by anticipating changes and adopting an appropriate approach to our work, we will accelerate a broad range of efforts to respond to the quality-related issues we are currently facing. These efforts include ensuring the quality of software, which is rapidly being introduced at a greater scale, reducing design and manufacturing processes dependent on people through the introduction of AI and the promotion of automation, striving to realize carbon neutrality and a circular economy with a focus on the future, establishing fundamental quality-related technologies that support advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and establishing quality evaluation criteria.
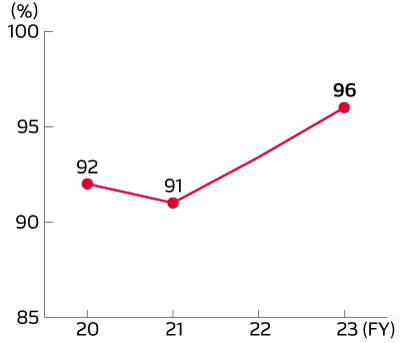
Employee Awareness Survey: DENSO CORPORATION
Question: Do you engage in your daily tasks by placing the highest priority on customers and quality?
Future Initiatives
Automotive technology, including advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), automated driving (AD), and connected cars, continues to evolve, but our desire to continue to provide high-quality products, systems, and services that prevent accidents remains unchanged. Moving forward, we will strengthen our future-oriented quality assurance systems and initiatives to continue providing society with high-quality products and services.