DENSO's SDGs
What are SDGs?
It is the common name for the Sustainable Development Goals , which are international goals adopted at the UN Summit in 2015 and targeted to achieve from 2016 to 2030. It consists of 17 goals for realizing a sustainable world, including "Building a Foundation for Industry and Technological Innovation" and "Creating a community where people can continue to live".
Contribution to SDGs for Materiality: Primary social issues
DENSO has selected primary social issues from among various ones and defined these issues as “Materiality.” Through our business activities, we are contributing to the achievement of the international goal that is the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by addressing selected issues related to “Environment,” “safety,” and “corporate foundation.”
We have also determined KPIs for each of our selected materiality. These KPIs are monitored and deliberated as Companywide targets by the Management Deliberation Meeting and the Board of Directors.
Examples of Initiatives through Business Activities
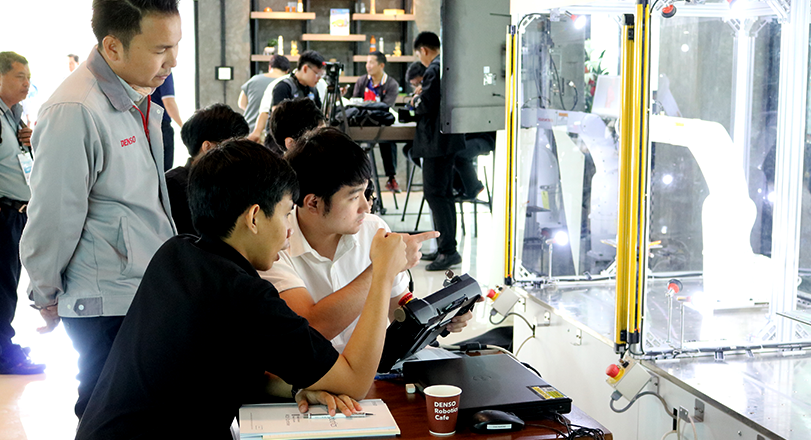

Training Lean Automation System Integrators through Collaboration between Japan and Thailand
We are conducting a demonstration project to train system integrators in Thailand by utilizing the highly efficient automated production system "lean automation" that we have adopted in our own production processes.
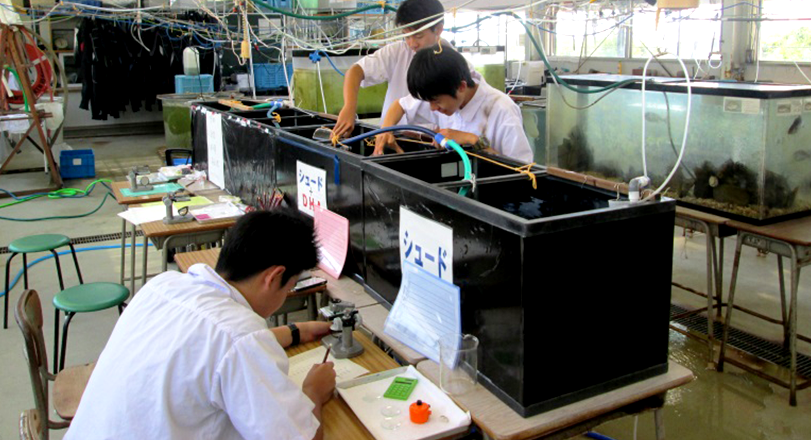

Making Use of the Natural Resources in Amakusa to Offer Educational Activities for the Next Generation
Leveraging the know-how in microalgae that we have cultivated through many years of research, we are promoting efforts to invigorate the regional industries of the city of Amakusa and develop the next generation of leaders who will oversee these assets in the future.
Commitment to the Environment
Vision
Contribute to an eco-friendly and sustainable society by reducing environmental burden and realizing highly efficient mobility
Reduce CO2 emissions from our factories to zero
Contribute to the electrification of automobiles and reduce our CO2 emissions to the greatest extent possible
Contribute to realizing a carbon-neutral society through technologies that collect and reuse CO2
Reduce environmentally harmful substances, emissions, and waste to help permanently preserve the global environment
Materiality: Primary social issues
Prevention of global warming
Prevention of air pollution/Reduction of environmental burden
Effective utilization of resources
Conservation of water resources
Related SDGs
| Fiscal 2023 | Fiscal 2024 | Fiscal 2026 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | Results | Targets | Targets | |
| Total emissions from Monozukuri activities (Scope 1 + Scope 2) Compared with fiscal 2021 |
25% reduction | 26% reduction | 50% reduction | 100% reduction |
| Popularization of products in the electrification domain (revenue) | ¥760.0 billion | ¥680.0 billion | ¥840.0 billion | ¥1 trillion |
〈Results for Fiscal 2023〉
-
Total CO2 emissions from Monozukuri activities:
Achieved targets through energy conservation, renewable energy generation (self-generation), the purchasing of renewable electricity from external sources, and the procurement of CO2 credits, in line with our plans. -
Popularization of products in the electrification domain:
Despite not achieving targets due to a decline in production at each OEM, which resulted mainly from semiconductor shortages and lockdowns in China, revenue increased year on year (fiscal 2022: ¥580.0 billion) owing to expanded sales of inverters and other products.
DENSO’s Environmental Strategies
Around the world, carbon-neutral initiatives aimed at transitioning from low carbon to carbon free have been accelerating.
In addition to further promoting its conventional environmental initiatives, DENSO aims to achieve carbon neutrality in its Monozukuri activities by 2025 with the use of carbon credits and by 2035 without the use of such credits.
Our initiatives aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2035 were outlined at DENSO DIALOG DAY (held in May 2021).
Examples of Initiatives
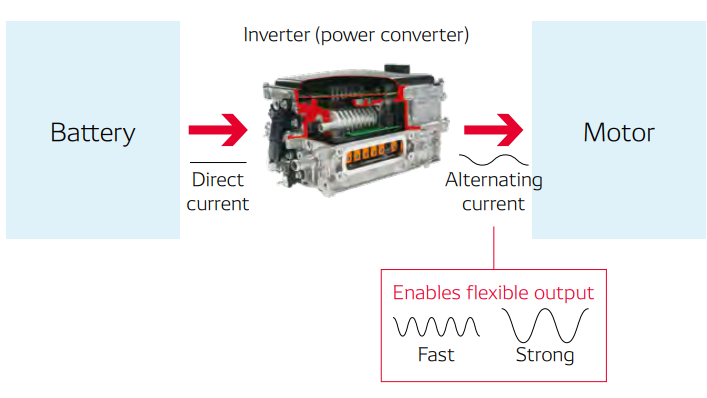
An inverter is a power converter device that converts direct current power from the battery to alternating current power and supplies that power to the motor for operation. The popularization of xEVs is an essential element in realizing the electrification of the mobility society, and inverters support the driving power of xEVs. Accordingly, enhancing the performance of inverters is the most important issue for car manufacturers. Inverters take in an electric current at a high voltage from the battery, and as such the semiconductor device generates a high level of heat. Figuring out how to keep the semiconductor device cool is the key to realizing smaller xEVs with higher performance as well as lowering their overall cost. To that end, we came up with the idea to cool the semiconductor device not from only one side, as had been done conventionally, but from both sides by making use of the heat exchange technologies that we have cultivated through the development of radiators. By doing so, we realized compact, highly efficient inverters.
DENSO is moving forward with the development of technologies that contribute to the promotion of vehicles powered by fuel cells, which use hydrogen to generate electricity. To date, many DENSO-developed products have been installed in the MIRAI, the FCEV manufactured by Toyota Motor Corporation. These products include high-voltage power system components, such as a power control unit and fuel cell boost converter, as well as cooling system parts, such as a radiator and cooling pump, that greatly improve cooling performance. Going forward, DENSO shall continue to utilize technology developed for hybrid, gasoline, and diesel vehicles in order to provide products that contribute to improving the reliability and performance of fuel-cell electric vehicles while at the same time reducing the cost of such vehicles.
With the aim of reducing its environmental burden, DENSO has been engaging in the research and development of resin materials that utilize the molecular structures of plants. We have also applied starch-based bio-polycarbonates and castor oil-based urethane resins in certain products. Plant-based resins do not make use of fossil fuels, making them a renewable resource. In addition, these resins are garnering attention due to the fact that they do not increase total CO2 volumes in the atmosphere even if they undergo thermal recycling. For many years, we have pursued the development of plant-based resins, and in 2009, we developed a castor oil-based radiator tank together with E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company. We are currently working to commercialize these radiator tanks and expand their installation in vehicles.
With the aim of achieving net-zero CO2 emissions from our plants, we are moving forward with the development to a CO2 circulation plant designed to capture and recycle CO2. In April 2021, we established demonstration equipment for such a plant inside the Electrification Innovation Center at the Anjo Plant and subsequently commenced a verification test.
The CO2 circulation plant is designed to capture CO2 primarily generated by the plant and recycle it as an energy source for the facility and for other uses. In the process, we have verified that the plant synthesizes methane, which is made from CO2 emitted by gas-fueled equipment, and hydrogen, which is produced by renewable electricity, and reused as a source of energy.
The CO2 circulation cycle of the demonstration equipment will be applied not only to the production facilities of DENSO but also to manufacturing sites in the world with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality.
Note: The technology used in this initiative was developed jointly with Toyota Central R&D Labs, Inc.
Related Content
We have established a long-term environmental policy "Eco Vision" to promote the resolution of environmental issues. Please see the details of EcoVision below.
EcoVision
Commitment to Peace of Mind
Vision
Contribute to a society where people can have peace of mind by eliminating traffic accidents and providing flexible and comfortable movement for all
Popularize safe products in order to eliminate traffic accidents
Address the need for ensuring a safe air environment and provide comfortable spaces
Support working people by offering technologies that help resolve issues stemming from the declining workforce
Provide safe and secure products that are of high quality to gain the trust and satisfaction of our customers
Materiality: Primary social issues
Reduction of traffic accidents
Provision of flexible and comfortable movement
Provision of safe and secure products
Response to decrease in birthrate and aging population
Related SDGs
| Fiscal 2023 | Fiscal 2024 | Fiscal 2026 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | Results | Targets | Targets | |
| Popularization of safety products (ADAS products) | ¥428.0 billion | ¥391.0 billion | ¥435.0 billion | ¥500.0 billion |
〈Results for Fiscal 2023〉
-
Popularization of ADAS products:
Despite not achieving targets due to a decline in production at each OEM, which resulted mainly from semiconductor shortages and lockdowns in China, revenue increased year on year (fiscal 2022: ¥360.0 billion) due to the expanded installation of such products as Global Safety Package 3.
DENSO’s Strategies toward Peace of Mind
The initiatives for achieving our vision of creating a secure society were outlined at DENSO DIALOG DAY (held in May 2021).
Examples of Initiatives
To help realize zero traffic accident fatalities, it is essential to further evolve safety products and install cutting-edge technologies in vehicles. It is also important to develop attractive products in terms of price and functionality and promote their widespread adoption in an even greater number of vehicles.
To that end, DENSO has developed the active safety system product Global Safety Package 3 (GSP3). To date, GSP3 has been installed in the HINO RANGER, the LEXUS NX, and the Toyota NOAH and Voxy, which were released in August 2021, October 2021, and January 2022, respectively.
Global Safety Package uses the combined performance of a millimeter-wave radar sensor and a vision sensor to assist the driver in controlling vehicle safety. The millimeter-wave radar sensor detects the shapes of objects, such as vehicles and road surfaces, while the vision sensor uses a camera to detect the environment ahead of the vehicle. GSP3 is the third generation of Global Safety Package.
By widening the scope of detection of the millimeter-wave radar and vision sensor and enhancing their detection performance, GSP3 is able to provide greater accident scenario coverage, including right and left turns at intersections and head-on collisions that were previously not covered, with accident scenario coverage range increasing dramatically from roughly 40% to nearly 70%. At the same time, we reduced the number and size of parts and expanded the settings in which GSP3 can provide accident prevention and driver support. We also worked to strike an optimal balance between light weight and low cost. In these ways, we are helping to popularize safety products.
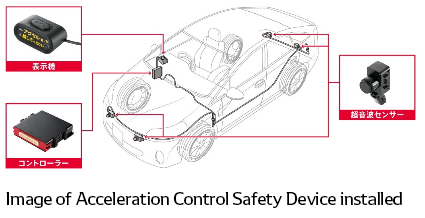
Recently, customers and greater society have been turning their attention to accidents resulting from drivers mistaking the gas pedal for the brake pedal as such accidents, primarily by the elderly, become an increasingly serious issue. To address this issue, DENSO and Toyota Motor Corporation jointly developed an acceleration control safety device to help prevent such accidents from occurring.
This product uses displays and buzzers to inform the driver when ultrasonic sensors attached to the bumper detect an obstacle in a vehicle’s course when the gas pedal is pressed while the vehicle is parked or stopped. If the driver continues to apply strong pressure to the gas pedal, mistaking it for the brake pedal, the device will limit acceleration to reduce the force of any resulting collision. Furthermore, if a driver is backing out of a parking space or otherwise putting their vehicle in reverse, the device will limit excessive acceleration if the gas pedal is pressed to an extent that would result in speeds of over 5 km per hour, even if an obstacle is not detected.
In 2020, DENSO developed “yuriCargo,” a driving scoring app for smartphones. Through this app, we have been promoting the yuriCargo Project, which aims to enhance safety awareness among drivers in collaboration with corporations and local governments.
yuriCargo makes use of information from accelerometers and GPS (Global Positioning Systems) already installed in smartphones to automatically detect driving behavior, such as sudden application of brakes, abrupt steering, sudden acceleration, speeding, and use of smartphone while driving, and provides the driver with a score after they finish driving. This score helps enhance the driver’s awareness of safety. For example, the yuriCargo Project offers traffic safety lessons based on driver score and provides discounts to local restaurants and mobility services for users with high scores. In addition, data acquired from the yuriCargo app can be put to use in the development of safer cities.
In 2023, we commenced the Iriomote Island yuriCargo Project on Iriomote Island, Okinawa Prefecture. With the aim of eliminating fatalities of the endangered Iriomote wildcat caused by vehicle traffic, this project seeks to boost safety awareness among drivers while at the same time leveraging the accumulated driving data from the yuriCargo app to develop safety measures and disseminate safety information. By doing so, this project will help reduce traffic accidents on Iriomote Island (the project runs from May 17, 2023 to March 31, 2024).
Labor shortages in the agricultural industry have become a global social issue. To address this issue, DENSO has been drawing on the technologies it has cultivated through its mobility products to implement measures to enhance the efficiency of agricultural work and to create new forms of agriculture in which humans work alongside machines.
Together with Asai Nursery, Inc., we established AgriD Inc. in 2018. At AgriD, we are proceeding with verification testing aimed at achieving highly productive and sustainable agriculture at large-scale smart farms.
For example, we are striving to create farms that make it easy for people who have trouble with physical labor to work, including by developing automatic harvesting robots, which can detect and determine the ripeness of target crops and harvest them automatically, and automated conveyer systems for harvested crops through the utilization of equipment cameras and AI technology. We are also striving to enhance the efficiency of personnel planning, stabilize work procedures, and improve the quality of harvested crops through work process management and guidance that draws on integrated production systems and tablet devices. In these ways, we are promoting the creation of next-generation greenhouse horticulture models.
Related Content
-
 Product development with safety as a top priority
Product development with safety as a top priorityQuality Control
-
 Global system for after-sales service
Global system for after-sales serviceAfter-Sales Service
Corporate Foundation Initiatives No.1
Vision
-
Ensure that each employee acts in a fair,honest,and ethical manner while complying with laws and regu-lations in each country and region
-
Provide safe and reliable products to customers,protect information assets,and prepare for cyber security risks that the "connected society"faces
Materiality: Primary social issues
Compliance
Information security
Related SDGs
| Fiscal 2023 | Fiscal 2024 | Fiscal 2026 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | Results | Targets | Targets | |
| Compliance Serious violations of laws |
None | None | None | None |
| Information security Serious incidents |
None | None | None | None |
-
Information security:
Recorded zero major incidents involving information security as we stepped up defense and detection measures amid the growing threat of cyberattacks across society.
Related Content
Corporate Foundation Initiatives No.2
Vision
-
Promote the development of "people," "organiza-tions," and "the working environment" to encourage our employees to maximize their abilities and work with enthusiasm and peace of mind
-
Respect the human rights of all our stakeholders, including our employees and people throughout our supply chain, in our business activities
-
Pursue business activities that take into account environmental issues, human rights issues, and compliance together with our suppliers
Materiality: Primary social issues
Empowerment of personnel (diversity and inclusion)
Healthy and safe working environment
Workstyle reform
Protection of human rights
Sustainable procurement
Corporate governance
Related SDGs
| Fiscal 2023 | Fiscal 2024 | Fiscal 2026 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | Results | Targets | Targets | |||
| Empowerment of personnel (diversity and inclusion) | Local employees in leadership roles at overseas bases | 20 employees | 20 employees | 21 employees | 20 employees or more | |
| Number of women in management positions at DENSO CORPORATION | Business fields | 145 | 139 | 160 | 200 | |
| Technical fields | 145 | 136 | 146 | 200 | ||
| Health | Employee Lifestyle Score at DENSO CORPORATION | 77 points | 74.5 points | 77 points | Over 77 points | |
| Safe working environment | Safety points *1 | Non-consolidated | 50.0 points | 23.0 points | 45.0 points | 40.0 points |
| Domestic Group | 36.0 points | 46.0 points | 31.5 points | 22.5 points | ||
| Overseas Group | 48.5 points | 24.5 points | 44.5 points | 36.5 points | ||
| Workstyle reform / Job satisfaction enhancement | Percentage of affirmative responses with respect to engagement *2 (non-consolidated) | 72% | 73% | 74% | 78% | |
| Protection of human rights / Sustainable procurement | Percentage of employees receiving human rights training (non-consolidated) | 100%* (new hires and new managers) |
100%* (new hires and new managers) |
100% (expansion to include production line managers and domestic Group companies) |
100% | |
| Corporate governance | DENSO will support the above targets for Materiality and progress to a more effective governance system as necessary based on factors such as social trends, changes to the external environment, and DENSO’s corporate culture. | |||||
*1 Safety points: Scoring depending on scale and type of accident. The lower the number the better the score.
*2 Work engagement: Implementation of annual survey regarding topics such as job fulfillment and organizational culture Ratio of employees who responded positively to survey questions regarding matters such as engagement toward work and workplace
〈Results for Fiscal 2023〉
-
Empowerment of personnel:
Strengthened efforts for global talent, such as holding global study sessions, assigning overseas personnel to important projects, and providing ongoing support at meetings concerning human resource development, making progress in line with our plans for fiscal 2023. -
Lifestyle Score:
Despite not achieving targets, continued to see ongoing improvements in yearly health behavior and health data. Through collaboration with each department, strengthened organization-oriented activities and support for employees at higher risk of health issues. -
Safety points:
Although non-consolidated and overseas Group company targets were achieved, did not achieve targets for domestic Group companies, as the number of disasters increased. In addition to analyzing causes of disasters, strengthened disaster-prevention activities by incorporating “reevaluation and reduction of risks pertaining to work done by people” and “reiterating the danger of touching any moving piece of machinery” into our key policies. -
Work engagement:
Achieved targets by improving engagement through such means as revamping career design initiatives in which we hold conversations with employees regarding their individual careers.
Examples of Initiatives
To continue to achieve growth while remaining a company that earns the trust of and inspires society, it is becoming even more important to promote diversity and inclusion, which means utilizing the strengths and perspectives of various employees from around the world. To that end, DENSO is promoting initiatives to realize a working environment and an organizational culture that enables an active and fulfilling role for diverse human resources in terms of gender, gender identity, sexual orientation, age, race, nationality, religion, and disabilities as well as unseen differences such as experience and value systems.
For example, in order to further expand our business on a global scale going forward, we are strengthening the development of local leaders who can oversee the future of DENSO and drive new business creation. We are also working to promptly discover outstanding personnel in collaboration with the head office and our overseas bases and are providing such talent with support through the Global Leadership Development Program and other initiatives.
In addition, we aim to provide fulfilling workplaces where employees can work with enthusiasm regardless of gender or gender identity. To that end, we are providing various kinds of career development support, including career development meetings between employees and their supervisors, women leadership training for newly appointed female managers, and role model roundtable discussions. Furthermore, in Vietnam, Malaysia, and other countries in Asia, where a large number of women work at our production sites, production lines adapted for pregnant women have been installed, enabling them to work while sitting down. By doing so, DENSO has created an environment where women at production sites can work energetically without experiencing stress during pregnancy.
Drawing on its strength of Monozukuri, DENSO has accumulated outstanding manufacturing capital such as its production bases across the globe and its frontline employees. To deliver even better products to our customers, we believe it is important to pass on the know-how we have accumulated on the front lines of Monozukuri and to realize highly efficient workplaces in which all employees can tackle new challenges.
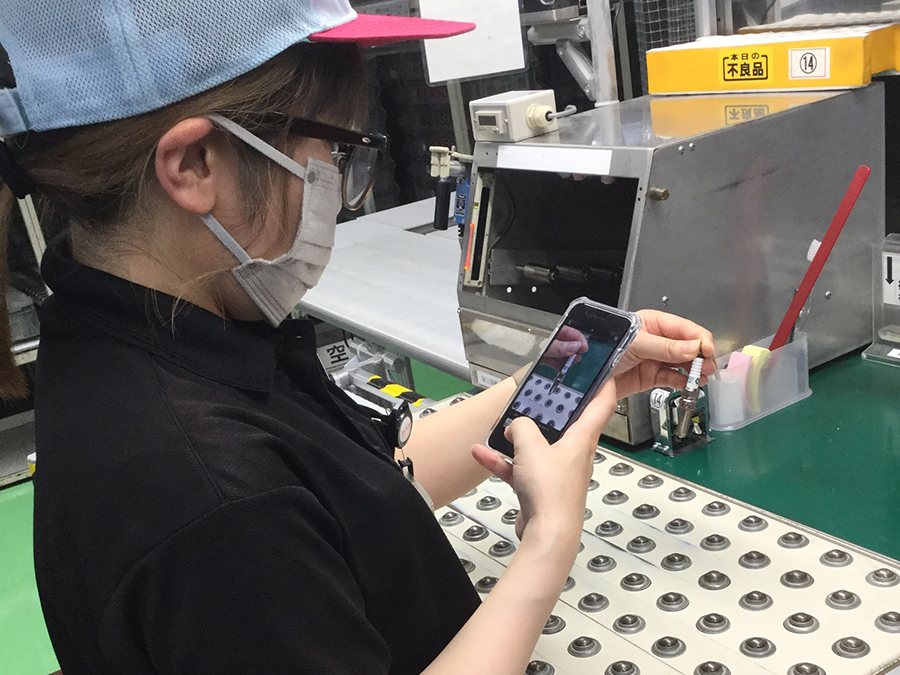
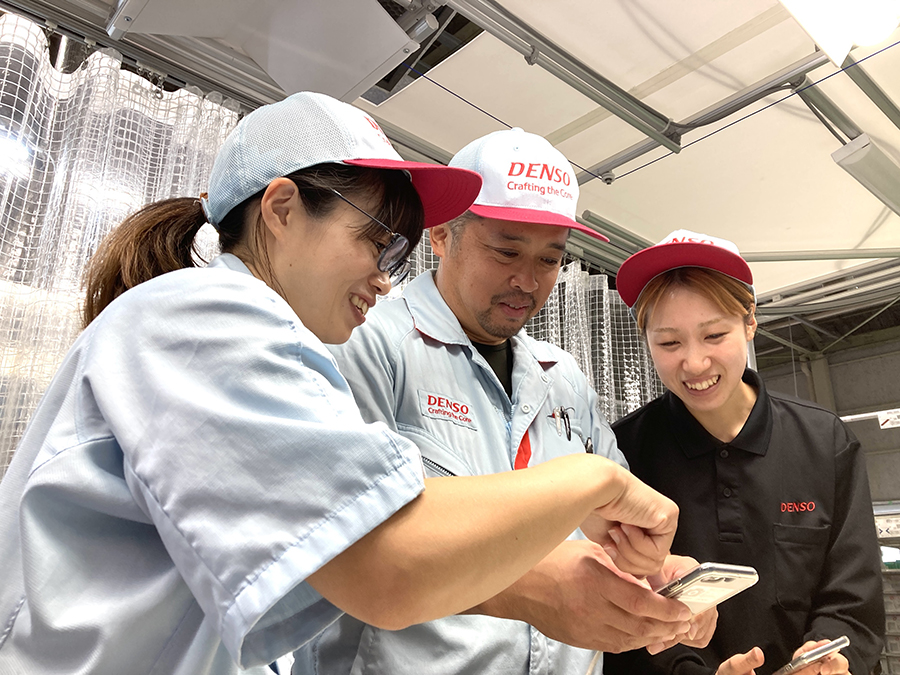
At DENSO CORPORATION, we have positioned the Daian Plant as a model plant. As of October 2022, we had provided the approximately 7,800 plant employees with digital devices, which are used in a variety of Monozukuri settings.
For example, when a defect occurs on the production line, these digital devices make it possible for all relevant personnel to be swiftly and accurately informed of the situation through the sharing of video and images. This, in turn, helps reduce the time it takes to fix the defect. In addition, by inputting figures such as part dimensions, which were previously managed on paper forms, into these digital devices, we are streamlining the process of receiving approval from managers and data analysis.
Furthermore, we hold morning meetings using digital devices in which we share information between all employees via video and images. Also, our young employees have been leading the way in providing instruction to their team members on how to use these digital devices. In these ways, the terminals have helped invigorate employee communication and have played an important role in enhancing workplace engagement.
Looking ahead, we will distribute these digital devices at even more locations, promote efforts to enhance each employee’s ability to utilize data, and make active use of the data we accumulate through these devices in various settings. By doing so, we will maximize DENSO’s Monozukuri capabilities.
Good physical and mental health underpins employees’ ability to feel energized in their work and is essential for ensuring the happiness of our employees and their families. DENSO positions promoting the health of its employees as an important management task and is practicing health and productivity management* for this purpose. In this regard, we announced our Health Declaration in September 2016. At the same time, DENSO is working to enhance its health-related initiatives from the perspectives of both physical and mental health to encourage workplace-level action and to improve employee health awareness.
Also, to promote health management at domestic and overseas Group companies, we formulated the DENSO Group Health and Productivity Management Basic Principles in February 2019. By sharing these principles globally and implementing health management activities based on the conditions at each company and in each country, we will improve the health awareness of all employees and establish a more comfortable working environment across the entire Group.

* “Health and productivity management” is a registered trademark of Nonprofit Organaization Kenkokeiei.
Related Content
-
 To continue to be a company that people syympathize with
To continue to be a company that people syympathize withEncouraging Diversity and Promoting a Work-Life Balance
-
 Various initiatives to respect human rights
Various initiatives to respect human rightsRespect for Human Rights
-
 Global efforts to continuously improve safety and health
Global efforts to continuously improve safety and healthSafety and Health
-
 Five Basic Rules for Achieving Optimal Global Procurement
Five Basic Rules for Achieving Optimal Global ProcurementThe DENSO Group's Procurement Policies